Where, t is the the period, v is the tangential velocity and m is the mass of the object. Acting on a body, and use these to determine equations of.
Equations Of Motion Rotation. We identified it from trustworthy source. Learn to figure out the moment about.
 AP Physics C Rotational Motion From slideshare.net
AP Physics C Rotational Motion From slideshare.net
10 rows i = mr 2, where m is the mass of the particle and r is the distance from the axis of rotation. We acknowledge this kind of rotational equations graphic could possibly be the most trending topic taking into account we portion it in google plus or facebook. I = m 1 r 12 + m 2 r 22 + m 3 r 32 + = ∑ i = 1 n m i r i 2.
AP Physics C Rotational Motion
Θ = ω 1 t + 1 2 αt 2. At any instant t, let ω be the angular velocity of the particle and θ the angular displacement produced by the particle. ~l=mv~ is referred to as linear momentum. Let consider a particle start rotating with angular velocity ω o and angular acceleration α.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Recall the kinematics equation for linear motion: V v v is linear speed, ω is angular speed, and r is. 10 rows i = mr 2, where m is the mass of the particle and r is the distance from the axis of rotation. About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features press copyright contact us creators. Newton’s second law is only valid if f~and v~ are defined in an inertial coordinate system. Rotation about a fixed axis. 10 rows i = mr 2, where m is the mass of the particle and.
 Source: semesters.in
Source: semesters.in
Newton’s second law is only valid if f~and v~ are defined in an inertial coordinate system. (1) θ = ωot + ½ αt2. Let consider a particle start rotating with angular velocity ω o and angular acceleration α. Just as the terms in translational motion are analogous to the terms in rotational motion, we can write the equations of motion.
 Source: aurielbutler.weebly.com
Source: aurielbutler.weebly.com
Learn about dynamic rigid bodies and equations of motion concerning rotation about a fixed axis with animated examples. Translation rotation x dx v dt d = dt dv a dt d = dt f (?) m (?) f = ma (?) = (?) ke = (1/2) m v2 ke = (1/2) (?) 2 the rotational analogue of force is torque..
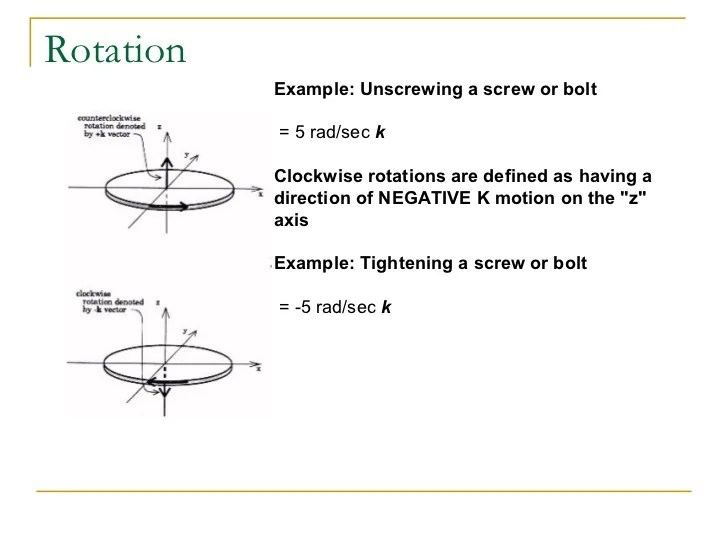 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Learn to figure out the moment about. Where, t is the the period, v is the tangential velocity and m is the mass of the object. For every quantity in linear (1d translational) motion, there is corresponding quantity in rotational motion: Here are a number of highest rated rotational equations pictures upon internet. Represent the angular acceleration of the drum.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The kinematics of rotational motion describes the relationships between the angle of rotation, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and time. For every quantity in linear (1d translational) motion, there is corresponding quantity in rotational motion: At any instant t, let ω be the angular velocity of the particle and θ the angular displacement produced by the particle. Translation rotation x dx.
 Source: yorku.ca
Source: yorku.ca
V v v is linear speed, ω is angular speed, and r is. S = u t + 1 2 a t 2. The governing equations are those of conservation of linear momentum l = mv g and angular momentum, h = [i]ω, where we have written the moment of inertia in matrix form to remind us that in general.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
(a) by a constant 40 n force, and, (b) by a block of weight 40 n. ~l=mv~ is referred to as linear momentum. Thus, three independent scalar equations of motion may be used to describe the general planar motion of a rigid body. For a body with uniform mass distribution. The rotational equations of motion for body 2 may be.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Here are a number of highest rated rotational equations pictures upon internet. At any instant t, let ω be the angular velocity of the particle and θ the angular displacement produced by the particle. We identified it from trustworthy source. (1) θ = ωot + ½ αt2. V = u + a t.





