Instead, it is known that the circle passes through a. (x2h)21 (y2k)25r2write the standard equation of a circle.
Equation Of A Circle Problems. X 2 + y 2 = 5. Ixl is easy online learning designed for busy parents.
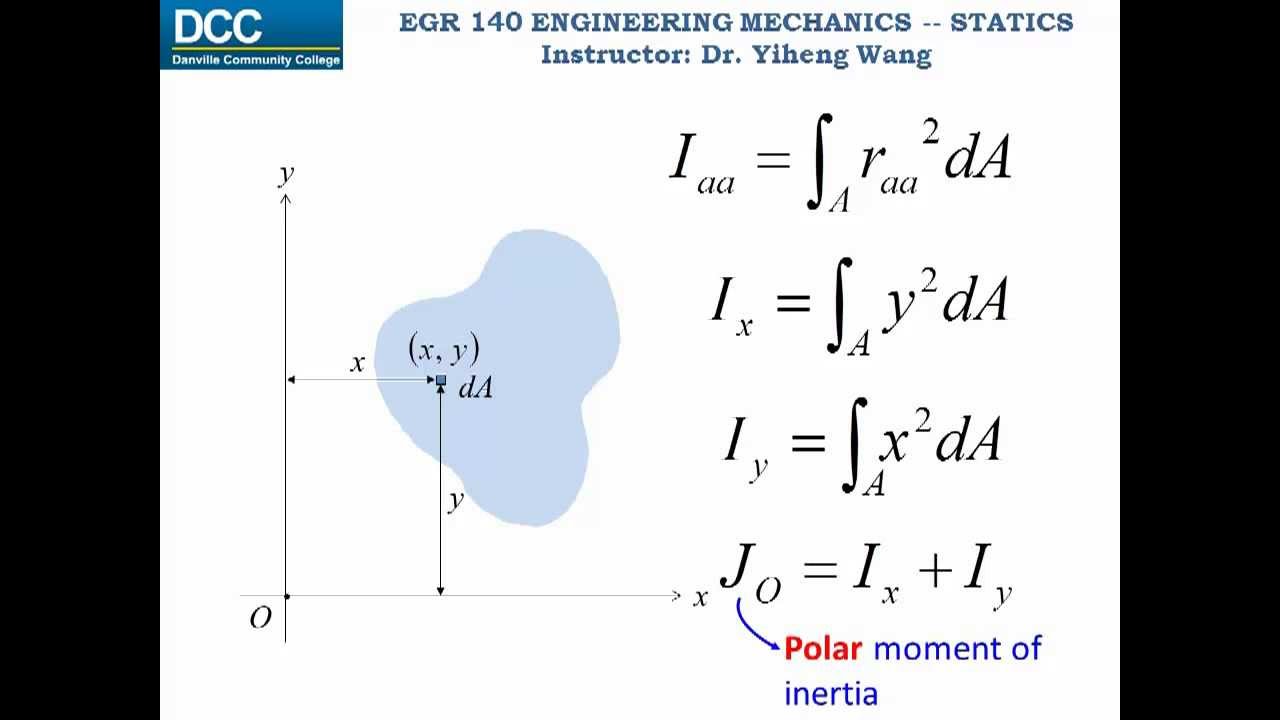 Statics Lecture 33 Area Moment of Inertia Calculation From youtube.com
Statics Lecture 33 Area Moment of Inertia Calculation From youtube.com
Ad we�re here to support your family! $({18/π})/2 = 9/π$ so the radius of our smaller circle is $9/π$. (18 , −13) and (4, −3) (x − 11)2 + (y + 8)2 = 74 12) center:
Statics Lecture 33 Area Moment of Inertia Calculation
X 2 + y 2 = 5. (x−9)2 +(y +4)2 =25 ( x − 9) 2 + ( y + 4) 2 = 25 solution. (x−h)2 +(y−k)2 = r2 ( x − h) 2 + ( y − k) 2 = r 2. 8/5/2018 equation of a circle problems 14/20 2 3x + 4y − 27 = 0.
 Source: hipwallpaper.com
Source: hipwallpaper.com
Write the standard form of a circle with radius 3 3 and center (0,0) ( 0, 0). Free online courses from the world�s leading experts since 2007 The center is at point ( 0, 0) \displaystyle (0,0) ( 0, 0) and r \displaystyle r r is its radius. Ad learn the applications of circles in geometry and the importance of.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
\displaystyle x^ {2}+y^ {2}=5 x2 +y2 = 5. If the center point and radius of a circle is given as (4, 5) and 7 respectively. (x−h)2 +(y−k)2 = r2 ( x − h) 2 + ( y − k) 2 = r 2. Substitute in the values r= 3,h =0,k = 0 r = 3, h = 0, k =.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Model problem 3 and 4 identify the coordinates of the center and the length of the radius in the circles below (x 5)2 + ( y+ 2) 2 = 4 radius: $({18/π})/2 = 9/π$ so the radius of our smaller circle is $9/π$. \displaystyle x^ {2}+y^ {2}=5 x2 +y2 = 5. The formula is ( x − h) 2 +.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Free online courses from the world�s leading experts since 2007 (x−a) 2 + (y−b) 2 = r 2. (x−h)2 +(y−k)2 = r2 ( x − h) 2 + ( y − k) 2 = r 2. The canonical form of the equation of a circle is. Instead, it is known that the circle passes through a.





