If the equation of a circle is given in the general form ax 2 + by 2 + cx + dy + e = 0, a ≠ 0, x 2.
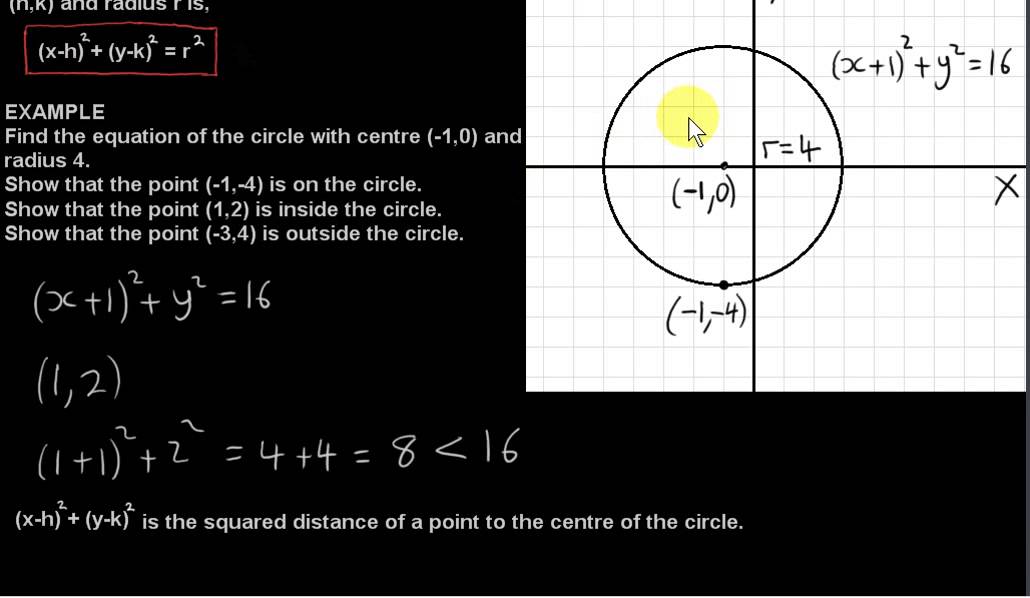
Equation Of A Circle Not Centered At The Origin. Write an equation of each circle described below. Notice that the center of the circle is not on the origin but rather at point (ℎ, 𝑘).
 Ex Find the Polar Equation of a Circle With Center at the From youtube.com
Ex Find the Polar Equation of a Circle With Center at the From youtube.com
Equation of a circle completing the square worksheet. The set of all points, p (x, y), that are a given distance, r, from a fixed point c (h, k). The general equation is x 2 + y 2 = r 2, so the equation when r = 4 is:
Ex Find the Polar Equation of a Circle With Center at the
The general equation of a circle with a center at. The general equation of a circle with a center at. In general, for a circle of radius r centered at the origin, its equation will. What is the equation of the circle centered at the origin with diameter 10?
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Circle centered at the origin. 1) if the center lies on the origin of the plane: We could plug in x = r cos θ, y = sin θ to convert to polar coordinates, but Thus, the equation of a circle with center at the origin is?? The circle has an equation.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Circle centered at the origin. If the circle were centered at the origin, of radius r, then r(cos$\theta$, sin$\theta$) traverses the circle once counterclockwise, for 0 $\le$$\theta$$\le$2$\pi$. The set of all points, p (x, y), that are a given distance, r, from a fixed point c (h, k). Therefore, the equation of the circle : At point 𝑃(?, ?) on.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
What if the circle were centered at, say, (x,y) = (5,2)? Let�s consider an arbitrary point ( x, y) on the circumference of the circle. Circle centered at the origin. Thus, we can say that this is the equation of the circle. We know the equation for a circle that has its center at the origin is r = x.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In this lesson, you learned the equation of a circle that is centered somewhere other than the origin is ( x − h) 2 + ( y − k) 2 = r 2 , where ( h, k) is the center. So in general we can say that a circle centered at the origin, with radius r, is the locus.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
But since this circle isn�t centered at $(0, 0)$, it means that certain lines with angle $\theta$ will never intersect the circle. This is the equation for a circle centered at the origin. If the equation of a circle is given in the general form ax 2 + by 2 + cx + dy + e = 0, a ≠.





