D = m ч v. It is the amount that velocity changes per unit time.
Equation For Velocity Gcse Physics. Using a kuala triangle.aqa p2.1 Moment = force x perpendicular distance from pivot.
 DistanceTime and VelocityTime Graphs GCSE Physics From youtube.com
DistanceTime and VelocityTime Graphs GCSE Physics From youtube.com
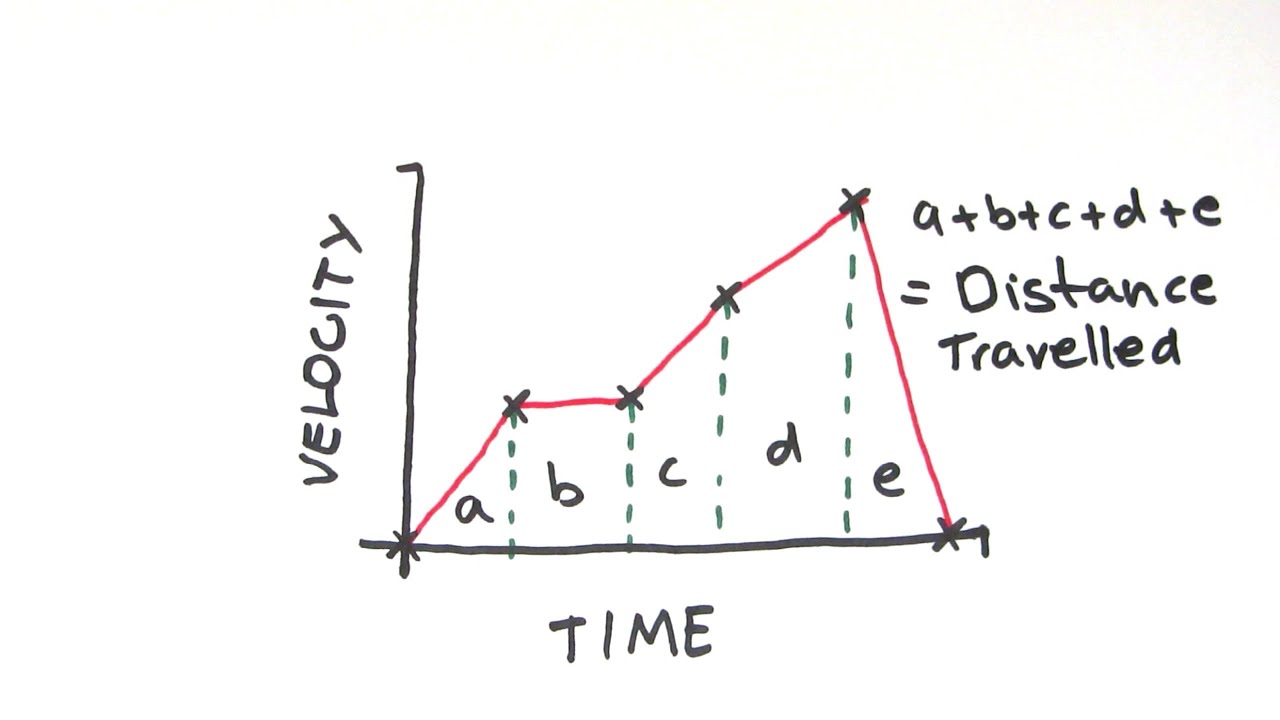
Awrobinson s image science for kids cool websites this or that questions. E k = 0.5 m v 2. In region b, the car is travelling at a constant velocity (the line has a gradient of zero).
DistanceTime and VelocityTime Graphs GCSE Physics
M = f x d. Ht = higher tier only p1 matter density = mass volume change in thermal energy = mass × specific heat capacity × change in temperature thermal energy for a change in state = mass × specific latent heat. We identified it from obedient source. This video defines velocity and acceleration and shows you how to perform simple calculations.
 Source: revisionworld.com
17 in the equation v2= u2 + 2as, what does the u represent? Calculate the new thinking and braking distances. This video defines velocity and acceleration and shows you how to perform simple calculations. We admit this kind of final velocity formula physics graphic could possibly be the most trending subject when we allocation it in google plus or facebook..
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Ht = higher tier only p1 matter density = mass volume change in thermal energy = mass × specific heat capacity × change in temperature thermal energy for a change in state = mass × specific latent heat. Gcse physics (8463) for use in june 2022 only. Distance moved average speed = time taken change in velocity ˛ vu °.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
V is final velocity in m/s. Speed and velocity are often mixed up when they should not be. Velocity is speed in a given direction. Calculate the new thinking and braking distances. The following equation shows the relationship between average speed, distance moved and time taken:
 Source: orvelleblog.blogspot.com
Source: orvelleblog.blogspot.com
Waves v = f x λ. Speed and velocity are often mixed up when they should not be. 2 ° ˝ 2 ˛˛ as ˙ They contain the following variables: Kinetic energy = 0.5 × mass × (speed)2𝐸k.





