Here are the conversion factors: Energy = power × time = vit.
Equation For Power Circuits. A plot of p(t) for various circuit elements is shown in.for a resistor, i(t) and v(t) are in phase and therefore always have the. This is kirchhoff’s second law, and is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy.
 From venturebeat.com
From venturebeat.com
Here are the conversion factors: (power equation) here, w = work done. The power formula is used to compute the power, resistance, voltage or current in an electrical circuit.
For any circuit element, the power is equal to the voltage difference across the element multiplied by the current. V = potential difference between two ends of a conductor. The average power of an ac circuit is called the true. Energy = power × time = vit.
 Source: venturebeat.com
Source: venturebeat.com
And r=e/i) that they are frequently credited to ohm. Two loads of magnitude 10kw each, are operating with a power factor 0.8 (each of them. P = i 2 r ; Remember, v = i × r. 1 w = 1 j/s.
 Source: venturebeat.com
Source: venturebeat.com
Power = current 2 × resistance. By ohm�s law, v = ir, and so there are additional forms. The unit for power is watt and the unit for energy is joules. Since the current and the voltage both depend on time in an ac circuit, the instantaneous power is also time dependent. Power measured in watts, symbolized by the letter.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
(power equation) here, w = work done. By ohm�s law, v = ir, and so there are additional forms. If you do your measurements on the cgs (centimeters, grams, seconds) system, force is expressed in dynes and work in ergs. In a closed loop of a circuit, the sum of electromotive forces is equal to the sum of the potential.
 Source: wikihow.com
Source: wikihow.com
If a voltage source (generating voltage v) is feeding power to resistor r, then the appropriate power equation will be p= (v×v)/r and resistance will be inversely proportional to power. (power equation) also, we can rewrite the power formula as, p =. We agree to this kind of power current resistance equation graphic could possibly be the most trending subject.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
For any circuit element, the power is equal to the voltage difference across the element multiplied by the current. The unit for power is watt and the unit for energy is joules. Since the current and the voltage both depend on time in an ac circuit, the instantaneous power p (t)=i (t)v (t) is also time dependent. 1 dyne =.
 Source: physics.stackexchange.com
Source: physics.stackexchange.com
However, these power equations are so commonly associated with the ohm’s law equations relating voltage, current, and resistance (e=ir ; P = f × s/t as we know, power = work done upon time p = w/t work = force ( f ) × displacement (s) p = f × s/t here, p = power. A plot of p(t) for.
 Source: nuclear.engie-electrabel.be
Source: nuclear.engie-electrabel.be
The power formula is used to compute the power, resistance, voltage or current in an electrical circuit. However, these power equations are so commonly associated with the ohm’s law equations relating voltage, current, and resistance (e=ir ; (power equation) also, we can rewrite the power formula as, p =. By ohm�s law, v = ir, and so there are additional.
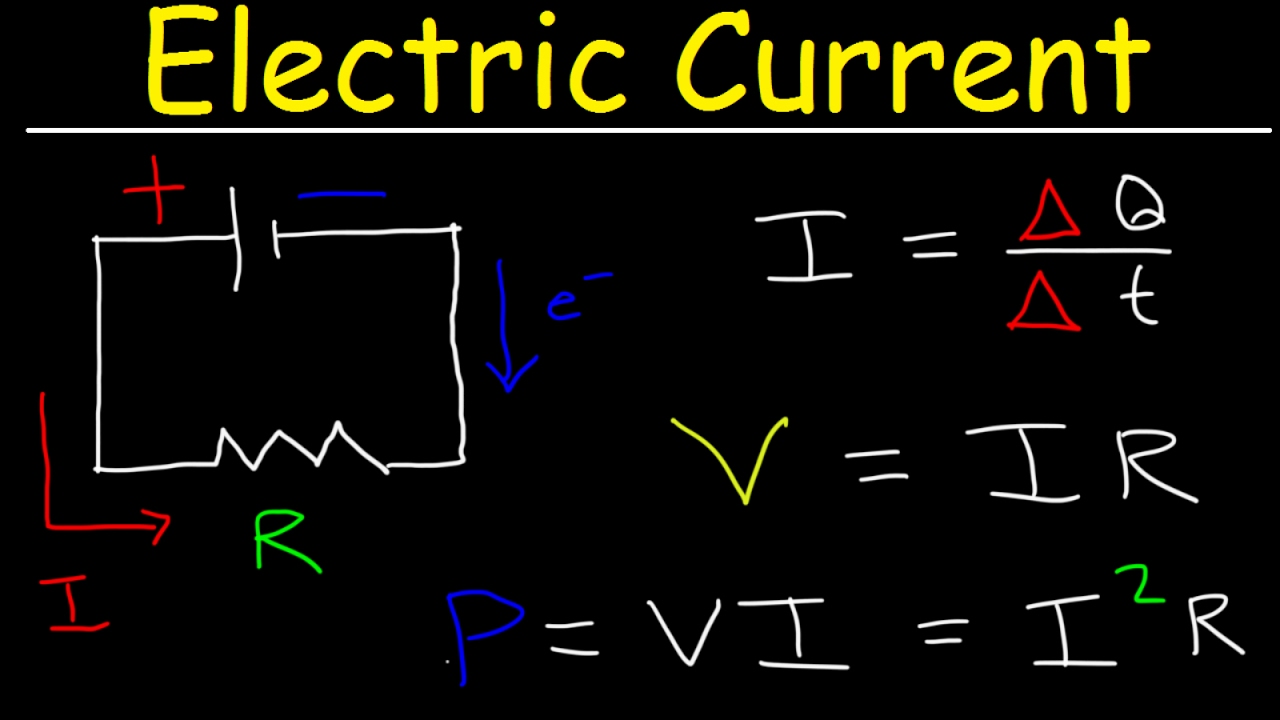 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
For any circuit element, the power is equal to the voltage difference across the element multiplied by the current. A circuit element dissipates or produces power according to where i is the current through the element and v is the voltage across it. In other words, energy = power x time and power = voltage x current. Two loads of.





