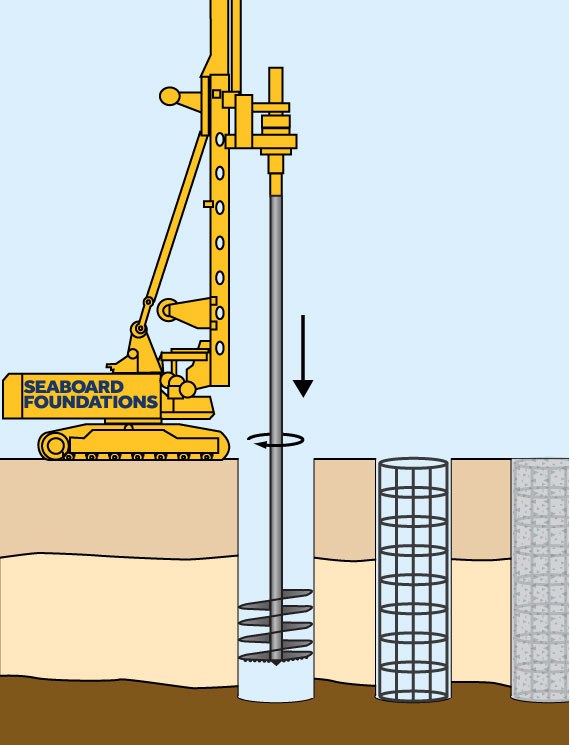
A cylindrical shaft is excavated, reinforcing steel is placed in the excavation and concrete is placed to form the shaft. A drilled shaft (caisson) is often installed in the construction.
Drilled Shafts Or Caisson Foundation. They are used to support structures with large axial and lateral loads by drilling cylindrical shafts into the ground which are then filled with concrete. The casing is a steel plate rolled and welded to form a large diameter pipe.
 Drilled Shaft / Caisson MorrisShea marine pile deep From morrisshea.com
Drilled Shaft / Caisson MorrisShea marine pile deep From morrisshea.com
Pier is inserted down to the bedrock. Caissons shall not be out of plumb more than 25 mm (1 inch) in 3000 mm (10 feet) for the full depth. As the name implies, temporary casings are used during the construction of drilled shafts and then removed afterwards.
Drilled Shaft / Caisson MorrisShea marine pile deep
Drilled shaft casings are also referred to as caissons, bored piles, or drilled piers. The additional capacity is a result of the size of the drilled shaft. Caissons shall not be out of plumb more than 25 mm (1 inch) in 3000 mm (10 feet) for the full depth. Extent of caissons into bedrock is shown on drawings, including locations, diameters of shafts, diameters of bells where required, estimated bottom elevations, and details of construction.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
The additional capacity is a result of the size of the drilled shaft. Cross sections of shafts and bells shall not be less than design dimensions. Caissons shall not be out of plumb more than 25 mm (1 inch) in 3000 mm (10 feet) for the full depth. They are used to support structures with large axial and lateral loads.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
Cross sections of shafts and bells shall not be less than design dimensions. Specifically, they are used to stabilize the drilled shaft excavation and then removed either after or during the placement of fluid concrete. A drilled shaft (caisson) is often installed in the construction of foundation piers for bridge, tower and harbor applications in marine pile environments. Only the.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
As the name implies, temporary casings are used during the construction of drilled shafts and then removed afterwards. The common reference to these foundations as “caissons” reflects the history of development of drilled shaft foundations. Atlantic city electric drilling shafts for light poles. Extent of caissons into bedrock is shown on drawings, including locations, diameters of shafts, diameters of bells.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
Install caissons with not more than the lesser of 1/24th of caisson shaft diameter or 75 mm (3 inches) from design center location. Extent of caissons into bedrock is shown on drawings, including locations, diameters of shafts, diameters of bells where required, estimated bottom elevations, and details of construction. Drilled shafts, also referred to as drilled piers, caissons or bored.
 Source: condrill.ca
Source: condrill.ca
The additional capacity is a result of the size of the drilled shaft. Drilled shaft casings are also referred to as caissons, bored piles, or drilled piers. As the name implies, temporary casings are used during the construction of drilled shafts and then removed afterwards. The history of caissons is long and storied, beginning more than a century ago, when.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
Pier is inserted down to the bedrock. The additional capacity is a result of the size of the drilled shaft. The history of caissons is long and storied, beginning more than a century ago, when caisson engineering was first used in the construction of massive bridges. The types of pier foundations are masonry or concrete piers and drilled caissons. Caissons.
 Source: morrisshea.com
Source: morrisshea.com
The casing is a steel plate rolled and welded to form a large diameter pipe. The types of caissons are box, open, pneumatic, monolithic, floating, excavated etc. A cylindrical shaft is excavated, reinforcing steel is placed in the excavation and concrete is placed to form the shaft. Drilled shafts (caissons or drilled piers) are typically high axial and lateral load.
 Source: civilengineerfriend.blogspot.com
Source: civilengineerfriend.blogspot.com
Install caissons with not more than the lesser of 1/24th of caisson shaft diameter or 75 mm (3 inches) from design center location. Casings are placed either before, during or after excavation. Drilled shafts are typically designed and constructed to support axial forces through a combination of side friction and end bearing. Casings are large enough in diameter to permit.





